If you're a project manager, it can be essential for you to identify and mitigate risks before starting a new venture. Conducting a RAID analysis can allow you to distribute tasks and justify the choices you make throughout the project's life cycle. Learning the significance of a RAID log can allow you to spearhead an organized assignment in the workplace and evaluate the success of your efforts. In this article, we define RAID project management, discuss its pros and cons and explore how to perform a RAID analysis for your next project.
What is RAID in project management?
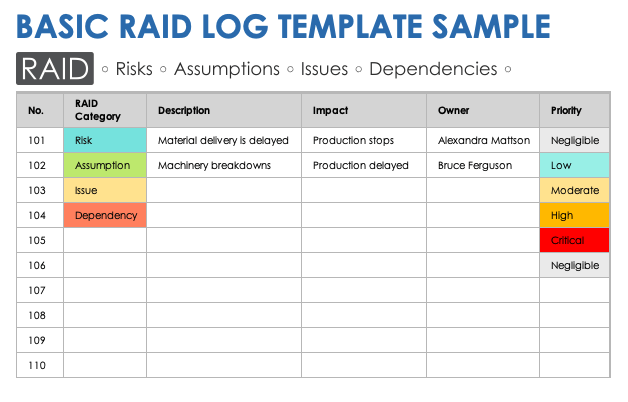
In project management, RAID is a technique that evaluates the effectiveness of a work assignment. A project manager often creates and adds updated information to a RAID log, which includes an agenda for completing tasks and satisfying the needs of stakeholders. The term RAID is an acronym that represents the following terms that apply to project management:
-
Risks: Risks represent potential challenges that can interfere with the success of the assignment. The RAID log explains the risks and their causes, discusses the effects they can have on the project's goals and develops strategies for avoiding and overcoming them.
-
Actions: Actions are the tasks team members plan to work on to deliver a quality final product. In this section, project managers identify the employees responsible for the tasks and the timeline for finishing them.
-
Issues: Issues are hardships project management teams have encountered in the past. The log explains how the issue transpired, who contributed to its occurrence and what team members did to resolve it.
-
Decisions: Decisions are choices the group made throughout the course of the project, which allow employees to track changes to their objectives. In the log, project managers may write what they decided on, who made the decision and when they agreed on the choice.
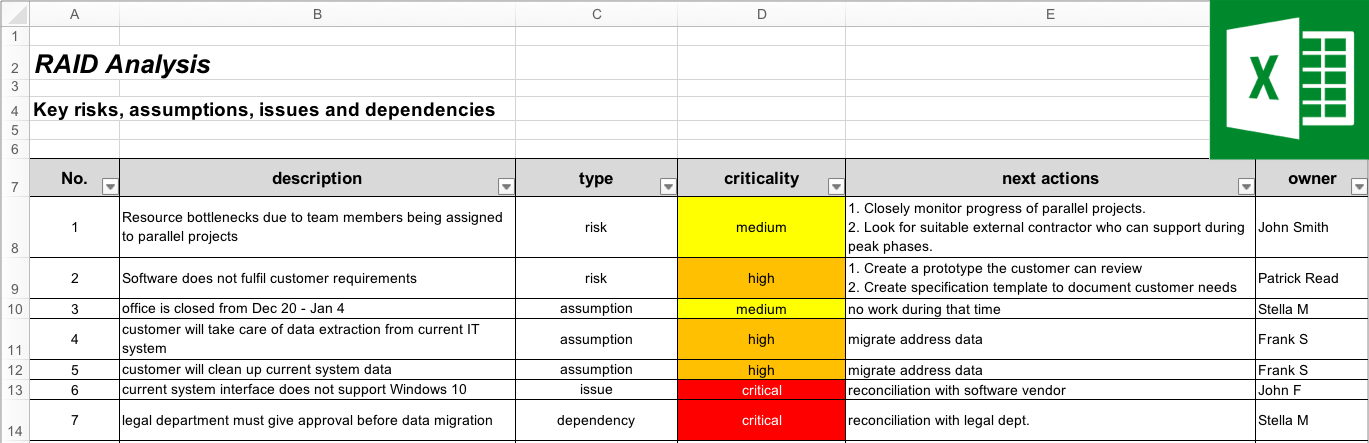
Project managers may also use a slightly different RAID model to coordinate their work initiatives. While risks and issues are still present, the other components differ. Here are alternatives that represent the "A" and "D" in the acronym:
-
Assumptions: Assumptions are concepts employees know are likely to be correct, although there's no tangible evidence to support them. For example, they may assume that they have enough financial resources to purchase supplies for their project.
-
Dependencies: Dependencies signify the connection between individual tasks in a project. The RAID log can note that professionals can't proceed to the second step until they finish the first step.
Why is using RAID important in project management?
Using RAID in project management is important because it helps you design a comprehensive plan for an assignment. You can strategize how to achieve the goals of the organization and direct members of your team to success. The analysis may require you to collect in-depth research, establish a timeline for your processes and justify every choice you make. You can also maintain accurate records of your activities to report to stakeholders and upper management. Each of these actions may be necessary to be an efficient project manager who can protect of interests of the company and its employees.
Advantages of conducting a RAID analysis
Composing a RAID log can be beneficial for your endeavors in the workplace. The advantages include:
Risk management
Performing a RAID analysis can help you feel more prepared about starting a new project. You can have confidence that you've considered potential challenges and have strategies in place to overcome them if they arise. For example, if you anticipate the client changing the deadline, then you know how to direct your teammates to work with more urgency.
Practicing risk management can also boost the confidence of your teammates. The more comfortable they feel contributing to an assignment, the higher the quality of work they may produce. You can empower them to believe the strength of your workflow can withstand extenuating circumstances.
Clear communication
Analyzing the components of a project can make it easier to communicate with a project management team and its stakeholders. Since a RAID log is shareable, you can distribute it to your teammates to ensure they're using the same information to complete their tasks. For example, instead of explaining a crucial decision you made, you can access the document to provide accurate details about what happened. The contents of the log may also address concerns the stakeholders may have, which can give them confidence in your leadership as a project manager. Clear communication can inspire teamwork and clarify your expectations.
Guidance
A RAID log can serve as a roadmap for leading a successful project. The risks section can allow you to predict potential challenges and avoid certain behaviors to remain focused on your goals. Both actions and assumptions can organize the workflow of the project management team, informing you of the next steps that can help you manage your time effectively. By documenting issues, you can learn from your mistakes and develop strategies to prevent them from reoccurring. Acknowledging dependencies can enable you to understand the purpose of your efforts, and justifying your decisions can strengthen your leadership.
Disadvantages of conducting a RAID analysis
There are also drawbacks to relying on a RAID log for a project. The disadvantages include:
Surplus of information
Since you may update the contents of a RAID often, it can contain a lot of information in one place. It can be challenging for you or your teammates to distinguish between the previous instructions and the new instructions. It may also increase the possibility that you overlook a significant detail. Confusion about what the analysis reported can influence the workflow of the team.
To remedy this disadvantage, it may be helpful to create multiple RAID logs that discuss the factors of one part of the project. You can deliver more specific information to individual teams, and they can see what details are most relevant to them.
Limited information
Another drawback is the limit of information on the RAID log, which can make the essence of the project more challenging to understand. For example, if you identify a challenge but don't explain how to mitigate it, then your teammates may encounter the obstacle with little instructions on minimizing its damage. It can be beneficial to find a balance between too much and too little detail. You can add updates that allow the reader to interpret your progress without overwhelming them with background information. Staying consistent in the writing style on the log as you proceed may also clarify ideas.
Time commitment
An effective RAID analysis has current information, but updating the content can require a lot of time. If you're working on a project with a strict deadline, it can be challenging to concentrate on your tasks while making sure you document your activities. Unbalance between reporting your work and completing your work can affect the quality of the project or the level of detail in the log. Learning how to prioritize urgent information for the analysis can help you save time when updating your records. You can also help your teammates save time when they consult the document.
How to perform a RAID analysis
Follow these steps to conduct a RAID analysis for a project management team:
1. Evaluate the severity of risks
Contemplate the challenges you may face once the project is underway. You can visualize the effect they can have on your team and your project's goals, which can help you determine their severity. For example, if inclement weather can delay the timeline for constructing a new building, then you may designate that as a severe risk. If you already have the materials you need, then a limitation of the budget may be a minor risk. Rating your obstacles can help you prepare to overcome them if they materialize. You can also monitor them as you make progress in the assignment.
2. Delegate actions to team members
Create an outline that assigns members of your team to specific tasks. Write their names and a description of the contributions you expect them to make. Specify a date and time you want them to submit their tasks, which may align with the overall timeline for the project. For example, if the initiative has different phases, then you may strive to satisfy certain milestones to ensure you're making adequate progress. Elaborate on the action section when you add additional tasks. Make sure the records are thorough enough to keep you and your teammates accountable for your productivity.
3. Track the occurrence of issues
Devote a section of the RAID log to project challenges you and your teammates experienced. Write about the signs you may have noticed before the issue impacted the assignment. If it escalates, add more detail to the log to describe the development. You can use these entries as guides for resolving problems for future projects. Remember to indicate if the issue is ongoing or stagnant, and discuss your technique for minimizing its effects. If the conflict was a risk that you identified at the beginning of the project, then you can also include it in this part of the analysis.
4. Substantiate the team's decisions
As you progress toward your project goals, you may make choices that affect the workflow of your team or the trajectory of your plan. Use the RAID log to document your decisions and monitor how the assignment has evolved. Include enough information to help your teammates and stakeholders understand what led you to the choice and why it was necessary to make it. For example, if you decided to purchase new equipment that exceeded the program's budget, your entry in the log can explain that the tools can accelerate the development process and boost the quality of the product.